Last Updated on December 18, 2024
To run a sump pump without electricity, consider options like manual pumps, battery backup systems, water-powered pumps, or gas-powered units. Manual pumps rely on your physical effort, using hand-cranks to remove water. Battery backups activate when power is lost, ensuring continuous drainage.
Water-powered pumps utilize municipal water pressure, while gas-powered options offer strong performance for heavy-duty needs. Each method has unique installation and maintenance requirements, so choose based on your specific situation. Explore the details behind these options for further helpful insights on setup and best practices.
Key Takeaways
- Use a manual sump pump, which operates without electricity by utilizing a hand-crank or lever mechanism.
- Consider a water-powered sump pump that uses municipal water pressure for operation, requiring no electricity.
- Install a battery backup system that activates automatically during power outages, ensuring continuous drainage.
- Regularly check and maintain the backup system’s battery to ensure it functions effectively during power failures.
- Keep the sump pit clean and free of obstructions to allow for efficient water removal by any pump system.
Manual Sump Pumps
A manual sump pump is a reliable solution when you lack electricity. These pumps depend on your physical effort to operate, making them vital during emergencies or in areas lacking a power source. Typically, they use a hand crank or lever mechanism to activate the pump submerged in the sump pit. Sump pumps are essential for preventing basement flooding and water damage, especially in homes with basements or below-grade areas.
Installation involves connecting the pump to a properly sloped discharge pipe and including a check valve to prevent backflow into the pit. While manual sump pumps are functional, they aren’t as efficient as electric or battery-powered versions. You’ll need to exert continuous physical effort, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming. This makes them more suitable for small-scale situations rather than high-water inflow scenarios.
Regular maintenance is important; you should routinely check for debris in the pump and pit, inspect the discharge pipe for blockages, and verify the check valve operates correctly.
Battery Backup Systems
When manual sump pumps can’t keep up with high water levels or you need an automated solution, battery backup systems become a practical choice. These systems work alongside your primary sump pump, activating during power outages or pump failures. They utilize a battery or battery bank, ensuring continuous drainage. Battery backup systems are essential for protection against basement flooding during power outages.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Audible Alarms | Alerts you to high water levels or activation |
| Remote Monitoring | Access via Pentair Home app for certain models |
| Battery Type | Wet cell marine batteries recommended |
These systems often include a power converter for smooth operation and are typically wall-mounted for space efficiency. Smart charging technology helps optimize battery life, while dual check valves facilitate maintenance. Regular checks during sump pump inspections are essential, as battery life can range from 3.5 to 6 days.
Various models are available, such as the Myers MBSP-2 and Basement Watchdog BWD12-120C, each designed for different capacities. Preassembled packages simplify DIY installation, ensuring you can handle unexpected flooding without electricity. Periodic testing of the entire system keeps it in peak condition, safeguarding your home from water damage.
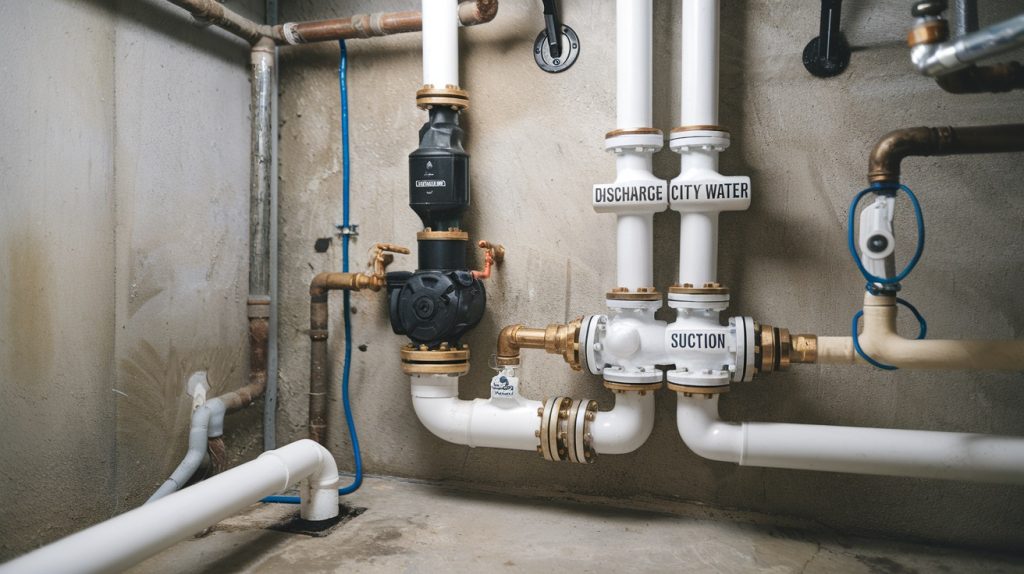
Water-Powered Sump Pumps
Water-powered sump pumps present an effective alternative for homeowners seeking a reliable, electricity-free solution to manage water accumulation. These pumps utilize municipal water pressure, relying on the venturi effect or Bernoulli’s principle to function. As water flows through a narrowed pipe, its velocity increases while pressure decreases, creating a vacuum that draws water from the sump pit. The combined waters are then expelled through a discharge pipe.
Key components include a pump jet, which converts municipal water pressure into suction, and a valve linked to a float switch that activates the pump based on water levels. This design features no moving parts in the pump jet, minimizing mechanical failures. Additionally, these pumps can use 1 gallon of tap water to remove approximately 2 gallons of floodwater, enhancing their efficiency in water removal.
Advantages of water-powered sump pumps include reliability during power outages, low maintenance requirements, and a consistent pumping rate that isn’t affected by battery degradation. However, you should consider the need for sufficient municipal water pressure and the potential increase in water bills due to continuous usage.
Gas-Powered Sump Pumps
While water-powered sump pumps offer a reliable solution for managing water without electricity, gas-powered sump pumps take it a step further by delivering more power and versatility. These pumps excel in heavy-duty applications, quickly moving large volumes of water—ideal for flood removal or draining construction sites. Their portability allows you to use them in various outdoor scenarios, including agricultural and construction tasks.
Gas-powered sump pumps typically feature trusted engines from reputable brands like Honda, Briggs, and Generac, ensuring reliability when you need it most. With horsepower ranging from 1.2HP to 8HP, they can achieve flow rates up to 265 GPM and lift capabilities of 148 feet.
Additionally, they are capable of pumping solids and debris, making them suitable for diverse environments. For safety, look for models with features like low-oil shutoff and self-priming designs. However, always remember to operate these pumps outdoors to avoid carbon monoxide risks.
When selecting a model, consider the total head lift and the diameter of the inlet and outlet to match your requirements. With durable materials and environmental compliance options available, gas-powered sump pumps offer a robust solution for various water management needs.
Hand Pump Techniques
To effectively set up a hand pump for your sump pit, start by selecting a suitable model and following the assembly instructions carefully. Once in place, you’ll need to operate it manually by pumping up and down to remove water efficiently. Additionally, having a backup sump pump ensures that you have a reliable solution in case of emergencies when power is unavailable.
Hand Pump Setup
A hand pump‘s effective setup is essential for guaranteeing reliable water access without electricity.
Begin by preparing your working area; make sure it’s clean, free from dust, and has enough space for tools and materials. Choose a spot where groundwater is readily available, ideally 50-60 feet away from septic tanks, adhering to local regulations. Consider the ground condition for ease of drilling. Additionally, ensure that the location you select is suitable for a sump pump as it can play a vital role in maintaining water access.
Next, assemble the hand pump according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Carefully attach the pump handle to the pump mechanism and use pump rods to connect it to the piston deep in the well. To guarantee a tight seal, apply Teflon tape on threaded connections, and use Loctite if recommended.
Measure the well depth with a measuring tape and determine the water level using a water level meter. Ensure the well is positioned above a water-bearing aquifer and install a well seal to protect the casing and pump riser pipe. Cut and connect PVC pipes to the required length based on the well depth. Finally, secure the pipes with appropriate fittings and test the pump to guarantee reliable water flow without potential contamination.
Manual Operation Tips
Effective manual operation of a hand pump requires careful attention to detail and technique to guarantee peak performance. Begin by verifying your hand pump is compatible with your sump system and located close to the sump pit for ease of access. Before you start, check for any damage or worn parts, and familiarize yourself with the operating mechanism. A sump pump’s float switch is crucial as it activates the pump when water accumulates, ensuring you can efficiently manage excess water during manual operation.
Here’s a quick reference table to guide you through the manual operation process:
| Step | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Prepare | Fill sump pit with water to activate the float switch | Verify sufficient water level |
| 2. Engage | Lift or turn the handle to create suction | Use smooth, consistent motion |
| 3. Pump | Move water out through the discharge pipe | Monitor water level closely |
| 4. Continue | Keep pumping until desired water level is reached | Check regularly |
| 5. Inspect | After use, check for wear, clean, and lubricate the pump | Maintain for longevity |
Combination Systems
Combination systems offer significant benefits by integrating multiple backup options for your sump pump, ensuring reliable operation during power outages. When considering installation, you’ll need to evaluate space requirements and potential costs, as these systems can be more complex and initially expensive.
However, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and damage prevention can make them a worthwhile investment. Additionally, incorporating a water-powered sump pump as part of your combination system can provide a dependable solution that operates without electricity during emergencies.
Benefits of Combination Systems
When it comes to safeguarding your basement from flooding, opting for a combination sump pump system offers unparalleled advantages. This system integrates both a primary AC sump pump and a battery backup pump, ensuring continuous operation during power outages or mechanical failures.
If the primary pump fails or loses power, the battery backup instantly takes over, providing critical support when you need it most. Enhanced protection is a key benefit. With dual float switches and a 24/7 monitoring controller, you minimize the risk of flooding. The system alerts you to any issues, ensuring proactive management.
Smart technology allows for real-time diagnostics, enabling you to monitor conditions remotely via a web browser or smartphone app. Another significant advantage is ease of use and maintenance. Pre-assembled systems simplify installation, while maintenance-free battery options reduce ongoing upkeep.
Installation Considerations and Costs
Installing a sump pump system can be a straightforward process, but it requires careful planning and attention to detail. To begin, you’ll need basic plumbing skills, as the installation is rated as moderate difficulty and typically takes 2-4 hours. Start by removing the existing pump, inspecting the sump pit, and then installing the new pumps and connections. Make certain you set up a battery box and secure all electrical connections properly.
You’ll need several materials, including a battery-operated backup sump pump kit, a deep-cycle 12-volt marine battery, PVC pipe and fittings, check valves, and stainless steel hose clamps. Teflon tape is also crucial for threaded connections.
Cost considerations are important; battery-operated backup sump pumps range from $100 to $1,000. While water-powered backup pumps may have higher initial costs, they can save on battery replacements. Installation costs vary based on setup complexity and local labor rates. Don’t forget that maintenance can add expenses, like battery replacements every 3-5 years and potential increases in water bills for water-powered systems.
Installation Considerations
Choosing the right location for your sump pump is vital for effective water management. Install it in the lowest area of your basement or crawl space, where water naturally collects. Being close to a power source is important; if necessary, hire an electrician to install a new outlet. Verify the pump’s location allows for easy access to a drainage pipe or suitable outlet for water removal.
Accessibility is key for maintenance and repairs, so pick a spot that’s easy to reach. Avoid placing the sump pump near underground pipes, cables, or service ducts to prevent obstructions. For safety, install the pump near a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet, and consider hiring a licensed electrician for wiring to comply with electrical codes. Don’t use extension cords; instead, secure power cords to the discharge pipe with tape or tie wraps. Confirm the motor is grounded according to local codes.
When digging the sump pit, make certain it’s deep enough for the basin and pump, and use a sturdy material for the basin. A concrete base with a hardcore layer at the bottom will provide the necessary support for peak operation.
Maintenance Requirements
To guarantee your sump pump operates effectively without electricity, regular battery checks are essential. You should also inspect manual components for any signs of wear or malfunction. Additionally, testing backup systems periodically will help you confirm everything is functioning properly when needed.
Regular Battery Checks
Regular battery checks are essential for guaranteeing your backup sump pump operates reliably during power outages. Start by selecting deep-cycle lead-acid batteries, such as marine or AGM types, which are suitable for extended discharge. Avoid standard vehicle batteries unless it’s an emergency, as they’re not designed for this purpose. Check your backup pump manual for the recommended maximum ampere-hour (AH) rating—around 120 AH is typically ideal. Additionally, consider using lithium-ion batteries for longer lifespans and fewer maintenance requirements.
Schedule maintenance every few months by checking water levels in traditional wet cell batteries and cleaning terminals twice a year to prevent corrosion. Test battery voltage every six months with a voltmeter to verify it’s fully charged and operational. Replace the battery every five years or as directed by the manufacturer.
To maintain charge, use a specialized trickle charger instead of a standard battery charger. Verify your main power supply is effectively charging the battery when operational. Monitor the pump’s run frequency to estimate battery lifespan during outages, and consider larger batteries or multi-battery systems for extended runtime.
Inspect Manual Components
Inspecting the manual components of your sump pump is essential for guaranteeing ideal performance and reliability. Start by checking the float switch and mechanism. Make sure the float switch moves freely, without contacting other equipment or the sump pit floor. For vertical float switches, confirm the lift rod moves up and down smoothly. Adjust the float stop if necessary to avoid continuous operation.
Next, clear any debris and obstructions. Remove debris from the sump pit bottom and the pump inlet screen. Ensure no floating debris interferes with the float switch. Check the discharge pipe for clogs and ensure the weep hole is clear to prevent airlocks. Additionally, it is crucial to review all instructions in the user manual to ensure proper understanding of operational guidelines.
Inspect the discharge pipe and connections as well. Ensure the discharge pipe is securely attached to the pump and check valve. Use primer and PVC cement for connections, but take care not to overtighten. Secure the power cord to the discharge pipe with cable clamps or zip ties.
Test Backup Systems
Testing backup systems is essential for verifying that your sump pump operates effectively during power outages or when the primary pump fails.
Regular testing helps you identify issues before they lead to water damage. Here are three critical areas to focus on:
- Power Outage Simulation: Simulate a power outage to confirm that the backup system activates automatically. Check if it switches to battery power seamlessly and that the pump starts working immediately. Monitor its performance throughout the test. Backup systems can mitigate risks during these outages, ensuring continued operation.
- Battery Charge and Health: Regularly check the battery charge level and use built-in indicators to assess its health. Perform a load test to verify it meets the pump’s power requirements. Replace the battery every 2-3 years or as recommended.
- Pump Performance and Capacity: Test the backup pump’s rate to verify it meets specifications. Evaluate its ability to handle expected water volumes during extended outages. Compare its actual performance against the manufacturer’s projections to ensure that it can manage heavy inflow during storms.
Best Practices for Use a Sump Pump Without Electricity
Utilizing best practices for your sump pump guarantees its reliability and efficiency, especially during critical times. To maximize performance, follow these essential steps:
1. Manual Activation: Regularly check the float switch by lifting it to verify it moves freely. This prevents malfunctions. Fill the sump with water to observe the pump in action, confirming it drains effectively outside your home.
2. Checking and Clearing Obstructions: Keep the sump pit clean. Remove debris from the bottom and the pump inlet screen. Verify the float switch is unobstructed and inspect the discharge pipe for any blockages. This helps maintain a clear path for water flow.
3. Verifying Proper Installation: Install a check valve to prevent backflow into the pit. Verify the discharge pipe slopes downward and drill an air bleed hole in the PVC pipe above the pump. Secure power cords if using electric backup, and make sure the pit cover isn’t pinching any wires.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Sump Pump Work During Extreme Cold Weather Conditions?
When it comes to sump pumps in extreme cold, you’ve got to guarantee they’re ready for the weather. If you don’t take the proper steps, you might find yourself in hot water later.
Make sure the discharge pipe slopes down to avoid freezing, and regularly check for debris that could block the pump. Installing a backup power source can also be a lifesaver, guaranteeing your pump runs smoothly when temperatures drop.
What Is the Lifespan of a Manual Sump Pump?
A manual sump pump typically lasts between 7 to 10 years with proper maintenance. However, some models can extend up to 20 years, especially if they’re regularly serviced.
Factors like the frequency of use, environmental conditions, and maintenance routines greatly influence their lifespan. To maximize longevity, make sure you inspect for wear and tear, clean the sump pit, and keep the pump well-maintained.
Are There Portable Sump Pump Options Available?
Absolutely, there are several portable sump pump options available. You can choose manual pumps for hands-on operation, or opt for battery-powered models that automatically kick in during power outages.
For heavier demands, gas-powered pumps deliver robust performance. Additionally, alternative power sources like generators or solar panels can enhance your sump pump’s versatility. With the right choice, you’ll guarantee effective water management, even in challenging conditions.
How Do I Know When to Replace My Sump Pump?
You should replace your sump pump if you notice signs of wear and tear, like increased noise or vibrations, or if you see corrosion or rust. If it’s over 5-7 years old, especially in high-use areas, consider a replacement.
Performance issues, such as slow water removal or frequent shut-offs, also signal a need for change. Regular maintenance checks will help identify these issues early, ensuring your pump operates efficiently.
Will a Sump Pump Help With Flooding in My Basement?
Yes, a sump pump can effectively help with flooding in your basement. It activates when water rises in the sump pit, using a float switch to pump water out and prevent overflow.
Regular maintenance is essential to guarantee proper operation, as debris can clog the pump. You must also check the installation of check valves and discharge pipes to maintain efficient water flow and avoid potential flooding issues in your basement.
Stay Flood-Ready: Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Sump Pumps
In summary, while traditional electric sump pumps offer convenience, exploring alternatives like manual and gas-powered options can guarantee you’re prepared for power outages.
Battery backup systems provide a safety net, while water-powered pumps tap into a renewable resource. Each method has its own installation and maintenance requirements, but the right choice balances efficiency and reliability.